Revolutionary Continuous Tyre Pyrolysis Plant Launched

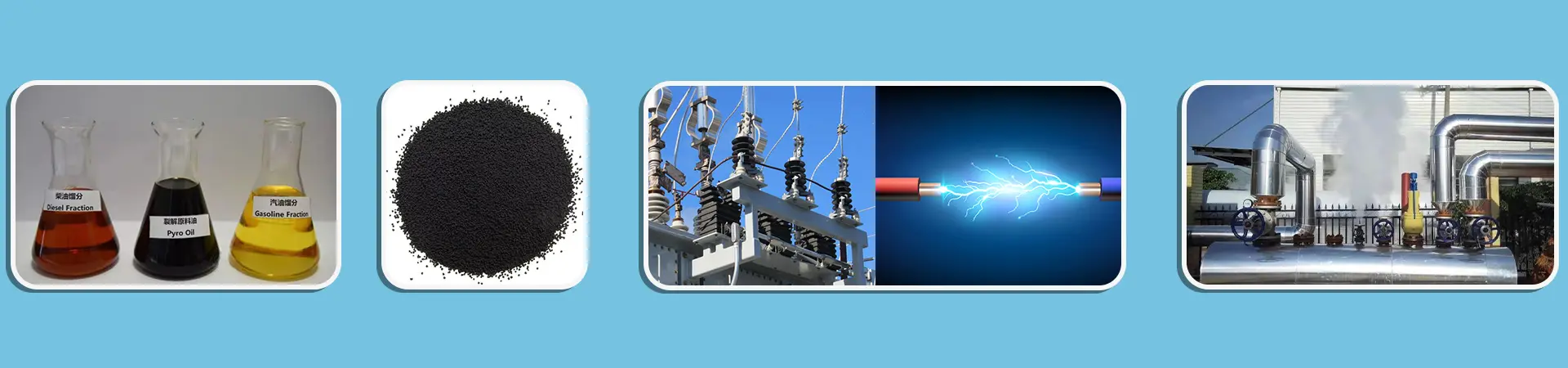
Carbon Black (CB) & Recovered Carbon Black (rCB): A Sustainable Shift in the Rubber Industry
Carbon Black (CB), a versatile material widely used in plastics, inks, paints, and rubber products (notably tires), accounts for a significant portion of global industrial fillers. However, recycling CB from end-of-life rubber—especially tires—remains challenging due to the inherent difficulties in rubber reprocessing, often relegating it to a disposable byproduct. Growing environmental concerns have spurred research into recovering CB from discarded rubber, aiming to reduce the industry’s ecological footprint. This article presents findings from an Artis-funded study and collaborative experiments by Michelin and Bridgestone, focusing on the properties of Recovered Carbon Black (rCB) and the urgent need to establish standardized evaluation criteria.
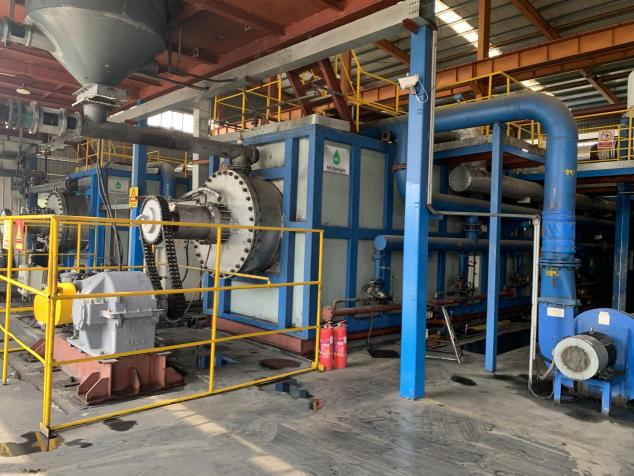

Revolutionizing Waste Recycling: The Rise of Continuous Screw Pyrolysis Plants
As global waste management challenges intensify, innovative technologies such as the Continuous Screw Pyrolysis Plant are transforming how industries process scrap tyres, plastics, and other non-recyclable waste into valuable resources. Thanks to its advanced engineering and high efficiency, this technology is being rapidly adopted across Europe, offering a sustainable solution to the world’s waste crisis.
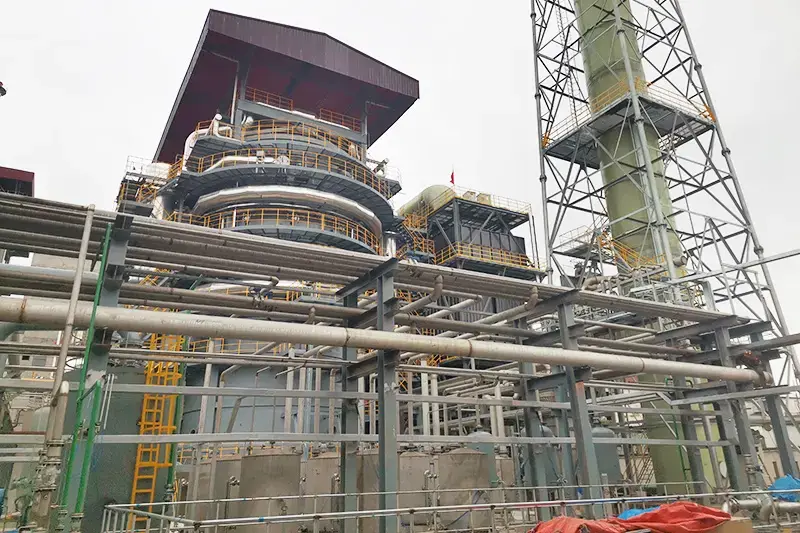

Turning Industrial Waste into Resources: Innovations in Wastewater, Emissions, and Solid Waste Management
As industries expand globally, the challenge of managing industrial wastewater, exhaust gases, and solid waste has become critical. Factories, power plants, and manufacturing units generate vast amounts of pollutants, but new technologies are transforming these byproducts into valuable resources—supporting both economic growth and environmental sustainability.
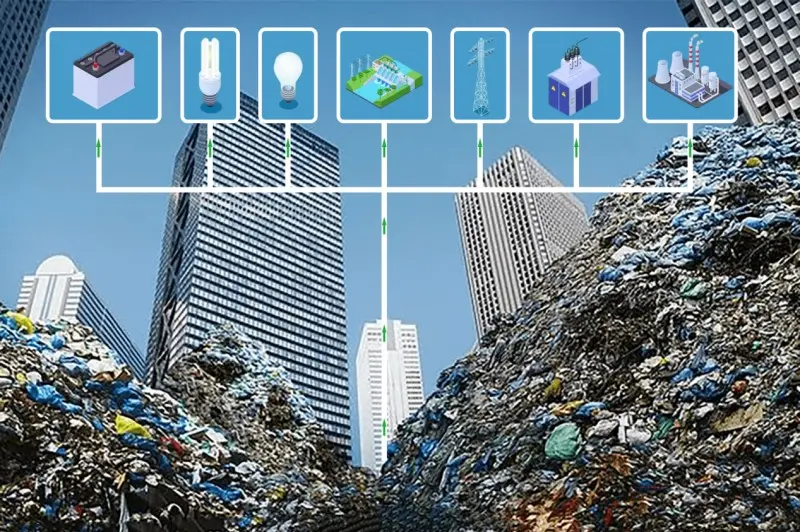

From Waste to Energy: A Sustainable Solution for Modern Cities
In the face of growing urbanization and increasing waste generation, cities around the world are turning to innovative technologies to tackle the dual challenges of waste management and energy production. Waste-to-energy (WtE) systems, which convert municipal solid waste (MSW) and household garbage into electricity, heat, or fuel, are emerging as a sustainable alternative to landfills and fossil fuels.

Recovered Carbon Black (RCB) Market Outlook: 2023-2032
EU Circular Economy Action Plan mandating 30% recycled content in tires by 2030
U.S. Inflation Reduction Act tax credits for pyrolysis infrastructure
APAC Extended Producer Responsibility laws (China's "Dual Carbon" policy, India's ELT recycling targets)
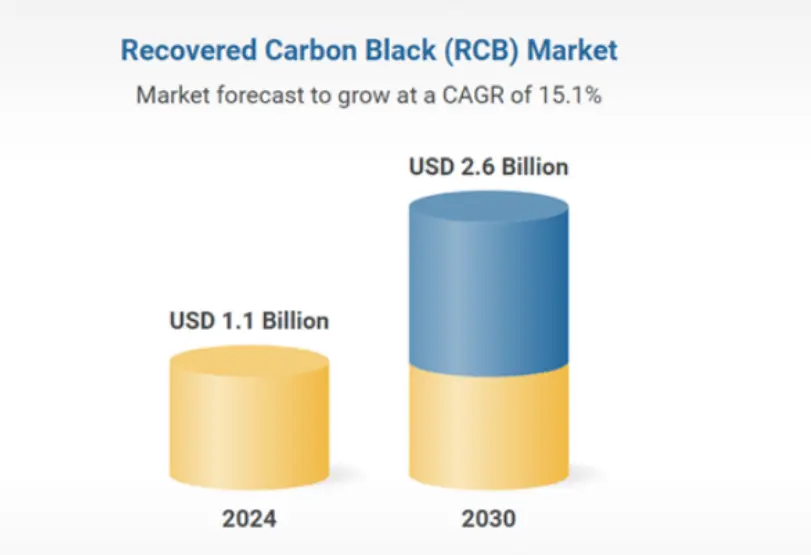
Recovered Carbon Black (rCB) - Global Strategic Business Report
The global Recovered Carbon Black (rCB) market, valued at US$1.1 billion in 2024, is projected to reach US$2.6 billion by 2030, growing at a robust 15.1% CAGR. This report delivers comprehensive analysis of market trends, growth drivers, and competitive forecasts to support strategic decision-making, including insights on recent tariff developments and their market implications.
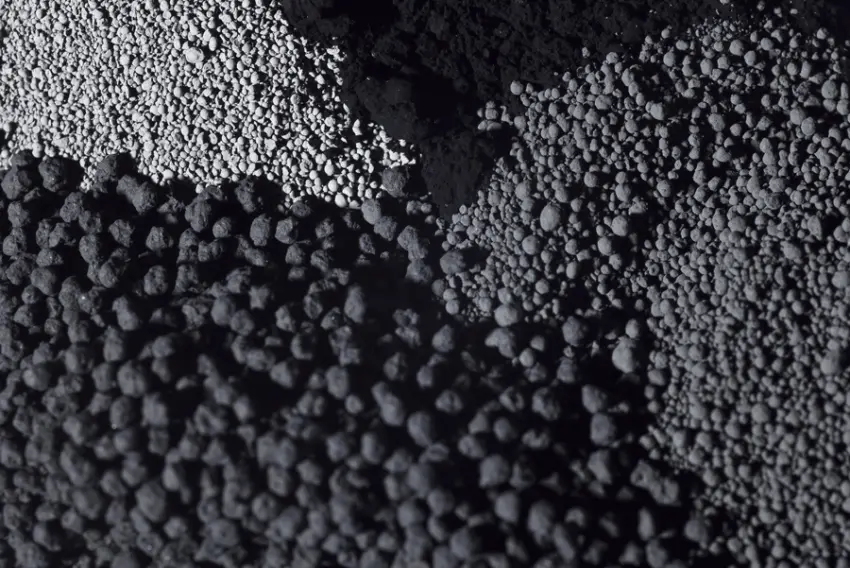

Carbon Black (CB) & Recovered Carbon Black (rCB): A Sustainable Shift in the Rubber Industry
Carbon Black (CB), a versatile material widely used in plastics, inks, paints, and rubber products (notably tires), accounts for a significant portion of global industrial fillers. However, recycling CB from end-of-life rubber—especially tires—remains challenging due to the inherent difficulties in rubber reprocessing, often relegating it to a disposable byproduct.
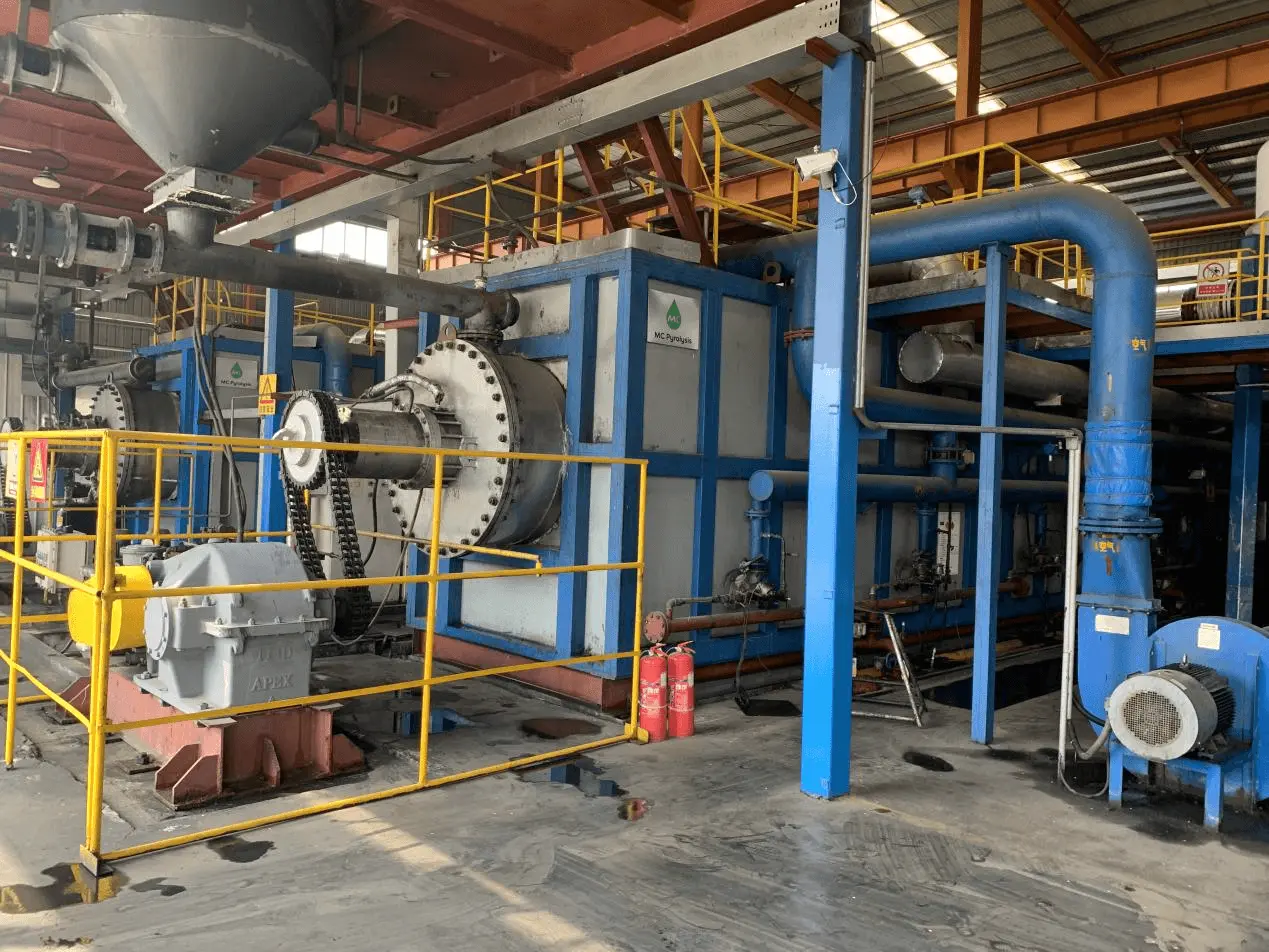

Revolutionizing Waste Recycling: The Rise of Continuous Screw Pyrolysis Plants
As global waste management challenges intensify, innovative technologies such as the Continuous Screw Pyrolysis Plant are transforming how industries process scrap tyres, plastics, and other non-recyclable waste into valuable resources. Thanks to its advanced engineering and high efficiency, this technology is being rapidly adopted across Europe, offering a sustainable solution to the world’s waste crisis.
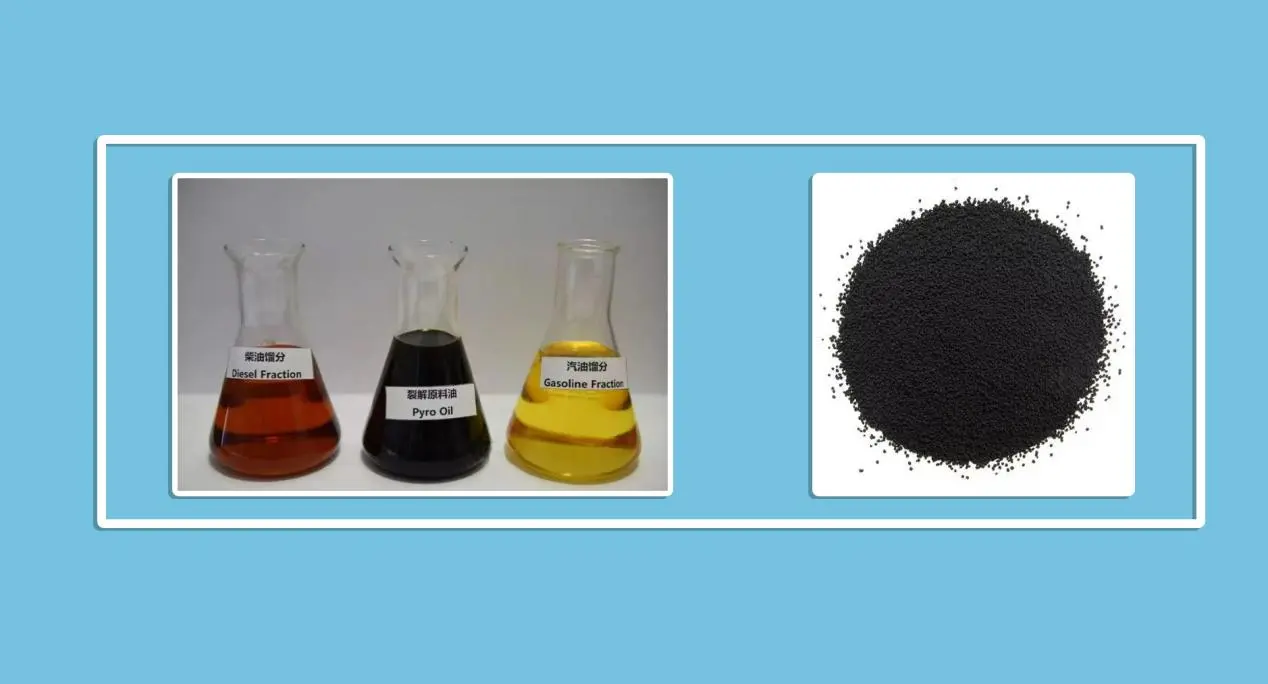

Driving the circular economy – tire pyrolysis oil at a legal turning point
Each year, well over a billion tires worldwide reach the end of their life. Many of these discarded tires still accumulate in landfills or are burned for a one-time energy gain, creating pollution and wasting valuable materials. Tire pyrolysis, a form of chemical recycling, breaks down end-of-life tires (ELT) into useful products like oil (TPO), gas, and recovered carbon black (rCB).

Huayuan Tech Showcases Innovative Tire Pyrolysis Solutions at 30th ETRA Conference in Brussels

Summary of European Policies on Tyre Pyrolysis
The European Union (EU) has implemented stringent regulations and policies to manage end-of-life tyres (ELTs), promoting recycling and recovery over landfilling. Pyrolysis, a thermal decomposition process that converts tyres into oil, gas, and carbon black, is recognized as a viable waste-to-energy and material recovery solution. Below is a summary of key European policies and initiatives related to tyre pyrolysis: