Turning Industrial Waste into Resources: Innovations in Wastewater, Emissions, and Solid Waste Management

As industries expand globally, the challenge of managing industrial wastewater, exhaust gases, and solid waste has become critical. Factories, power plants, and manufacturing units generate vast amounts of pollutants, but new technologies are transforming these byproducts into valuable resources—supporting both economic growth and environmental sustainability.
The Growing Challenge of Industrial Waste
Industrial activities contribute significantly to pollution:
Wastewater: Contaminated with heavy metals, chemicals, and organic pollutants, industrial effluent threatens aquatic ecosystems.
Exhaust gases: Emissions like CO₂, SO₂, NOx, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) worsen air quality and climate change.
Solid waste: Sludge, scrap metals, and non-recyclable materials often end up in landfills, wasting potential resources.
Without proper treatment, these wastes pose severe health and environmental risks. However, innovative circular economy approaches are changing the game.
From Wastewater to Clean Water and Energy
Advanced treatment methods are making industrial wastewater reusable:
Membrane filtration & reverse osmosis – Remove toxic chemicals and heavy metals for safe discharge or reuse.
Electrochemical treatment – Breaks down pollutants using electric currents, recovering metals like copper and zinc.
Anaerobic digestion – Converts organic wastewater into biogas, a renewable energy source.
Success Story: In Singapore, NEWater plants treat industrial wastewater to ultra-pure standards, supplying 40% of the nation’s water needs.
Cleaning the Air: Turning Exhaust into Raw Materials
Instead of releasing harmful gases, industries are capturing and repurposing them:
Carbon Capture and Utilization (CCU) – Converts CO₂ into fuels, plastics, or construction materials.
Scrubbing technologies – Remove sulfur and nitrogen oxides, turning them into fertilizers (e.g., gypsum).
Thermal oxidation – Destroys VOCs while recovering heat for energy.
Example: Norway’s CarbonQuest captures CO₂ from cement factories and stores it underground or sells it for carbonation in beverages.
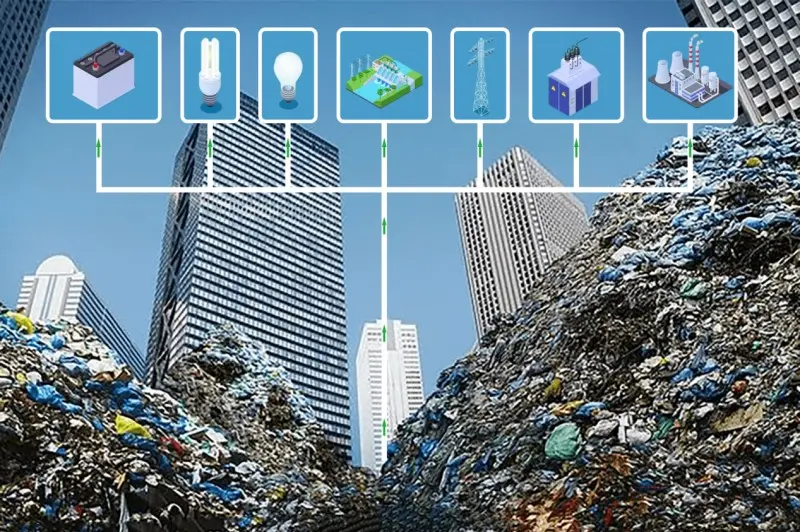
Solid Waste: From Landfill to Profit
Industrial solid waste is being repurposed through:
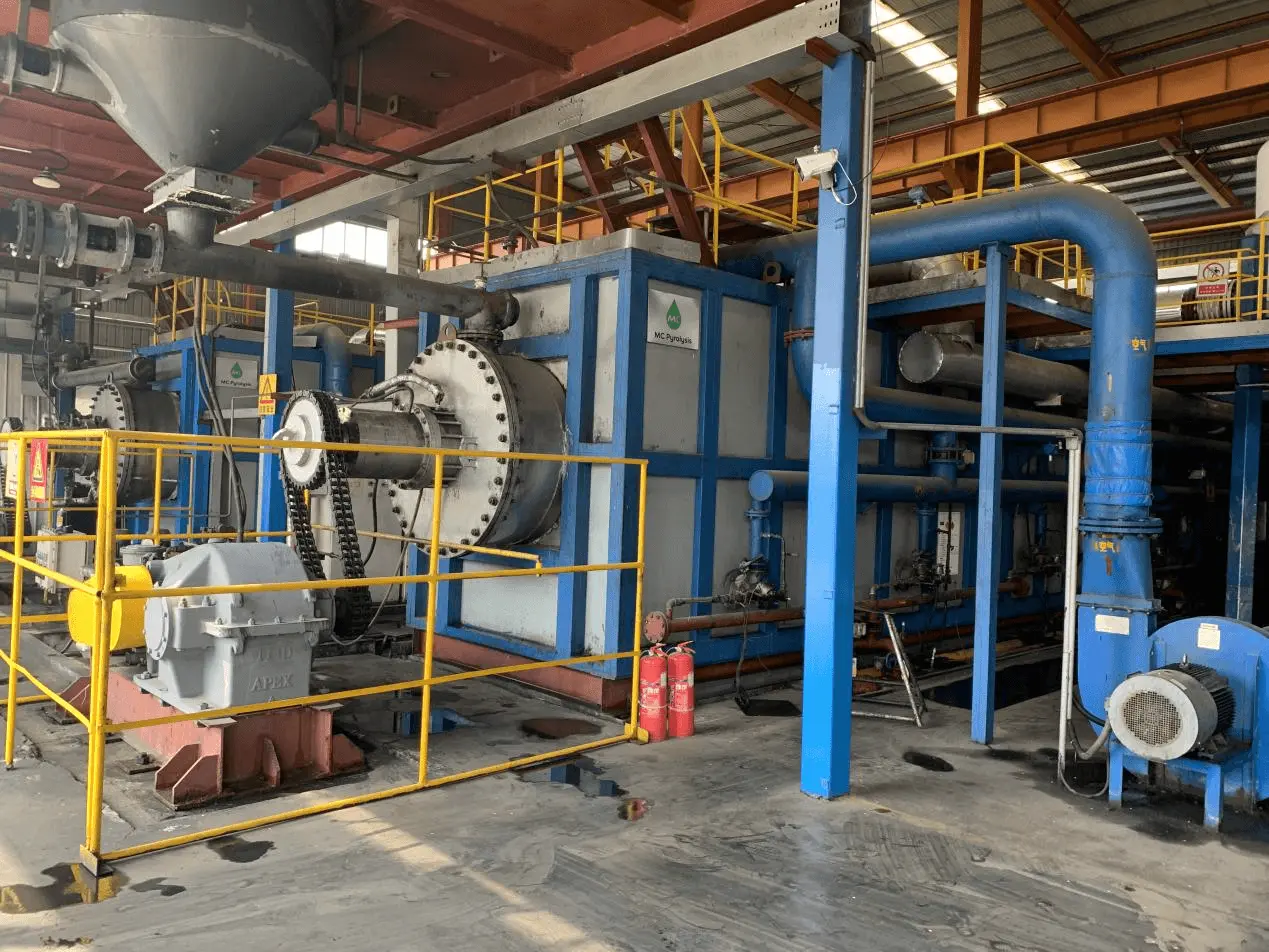
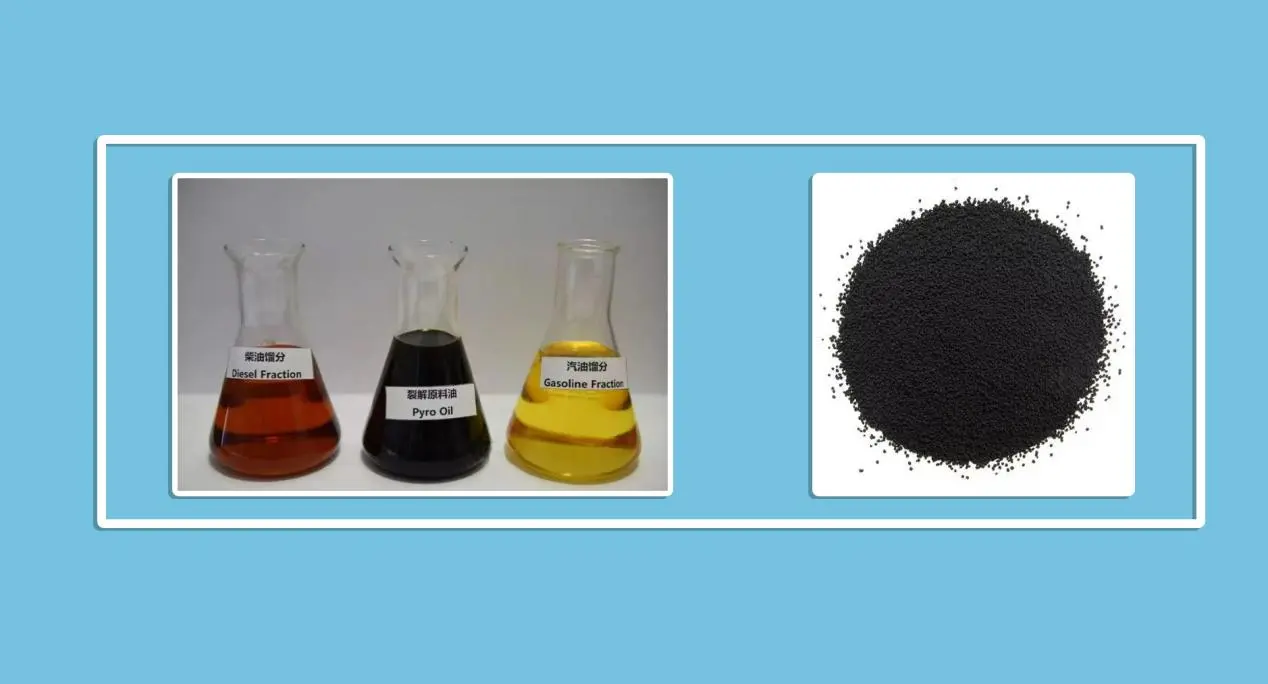
Pyrolysis & gasification – Converts plastic and Rubber Waste into synthetic fuels.
Metal recovery – Smelters extract precious metals from electronic waste (e-waste).
Waste-to-cement – Hazardous residues are used as alternative raw materials in cement production.
Case Study: Japan’s Eco-Town initiative recycles 98% of industrial waste, including turning incinerator ash into construction materials.
The Road Ahead: Policy and Innovation
While progress is being made, challenges remain:
✔ High costs – Governments must incentivize green tech adoption through subsidies.
✔ Stricter regulations – Policies like the EU’s Industrial Emissions Directive push industries toward zero waste.
✔ Corporate responsibility – Companies like Tesla and Unilever are committing to zero-waste manufacturing.
Conclusion
Industrial waste is no longer just a burden—it’s a resource waiting to be tapped. With advancements in recycling, carbon capture, and waste-to-energy, industries can reduce pollution, cut costs, and contribute to a circular economy. The future lies in seeing waste not as trash, but as the foundation of sustainable innovation.
The best way to predict the future is to invent it—starting with our waste.
Would you like a focus on specific industries (e.g., textiles, mining) or regional examples (e.g., China’s policies, EU tech)?