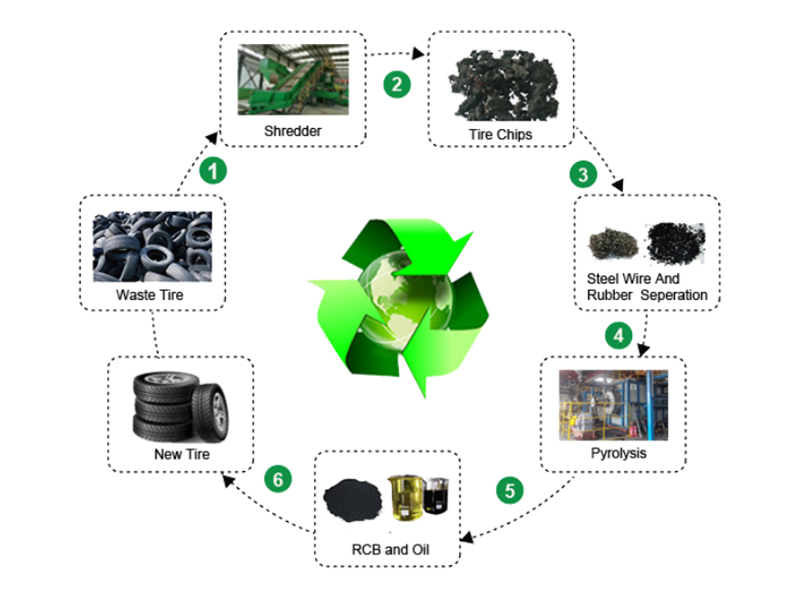
Solution of MSW to energy

Overview of Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) Trends:
Over the past several decades, the generation and management of municipal solid waste (MSW) have undergone significant changes. MSW generation increased steadily—except during periods of economic recession—from 88.1 million tons in 1960 to 292.4 million tons in 2018. Between 2005 and 2010, generation declined by 1 percent, followed by a 7 percent increase from 2010 to 2017. The rise from 268.7 million tons in 2017 to 292.4 million tons in 2018 was largely due to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) incorporating additional food management pathways.
In terms of per capita waste generation, the rate was 2.68 pounds per person per day in 1960. It rose to 3.66 pounds in 1980, peaked at 4.74 pounds in 2000, and slightly declined to 4.69 pounds in 2005. By 2018, the rate had reached 4.9 pounds per person per day, representing an 8 percent increase from 2017. This rise is primarily attributed to the EPA’s expanded accounting for food waste management.

Recycling and composting rates have also shown notable growth over time. In 1960, only a little over 6 percent of MSW was recycled or composted. This figure rose to about 10 percent in 1980, 16 percent in 1990, 29 percent in 2000, and peaked at 35 percent in 2017. However, it slightly declined to 32.1 percent in 2018.
Waste-to-energy practices have also evolved. The proportion of MSW combusted with energy recovery grew from zero in 1960 to 14 percent in 1990 and stood at around 12 percent in 2018.
Landfilling has seen a dramatic decline, falling from 94 percent of generated waste in 1960 to 50 percent in 2018.

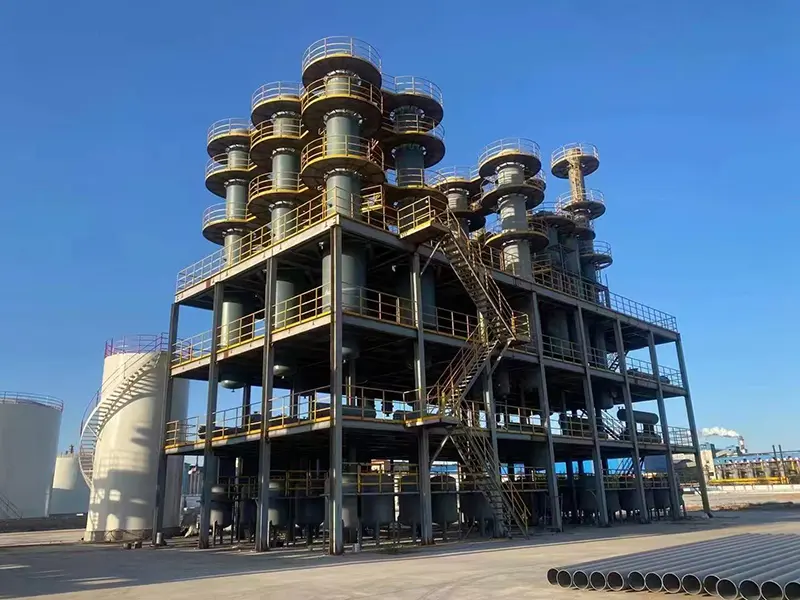
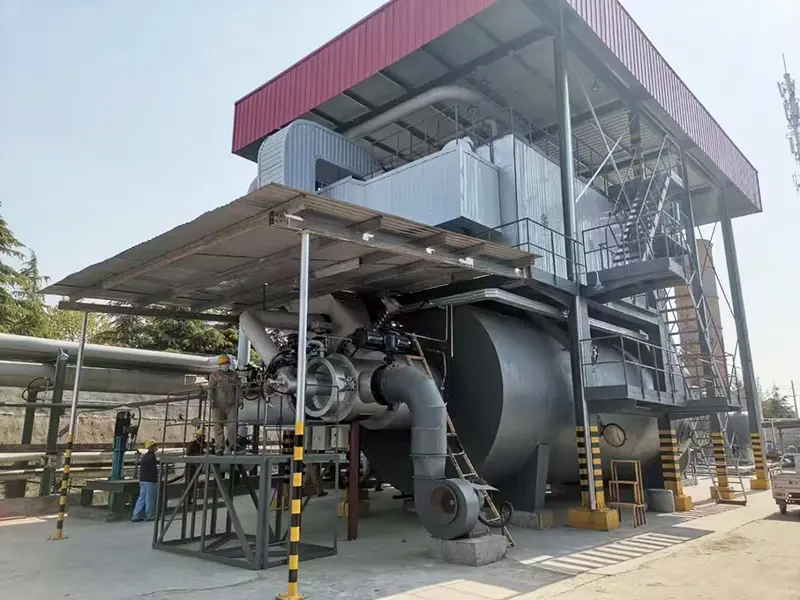
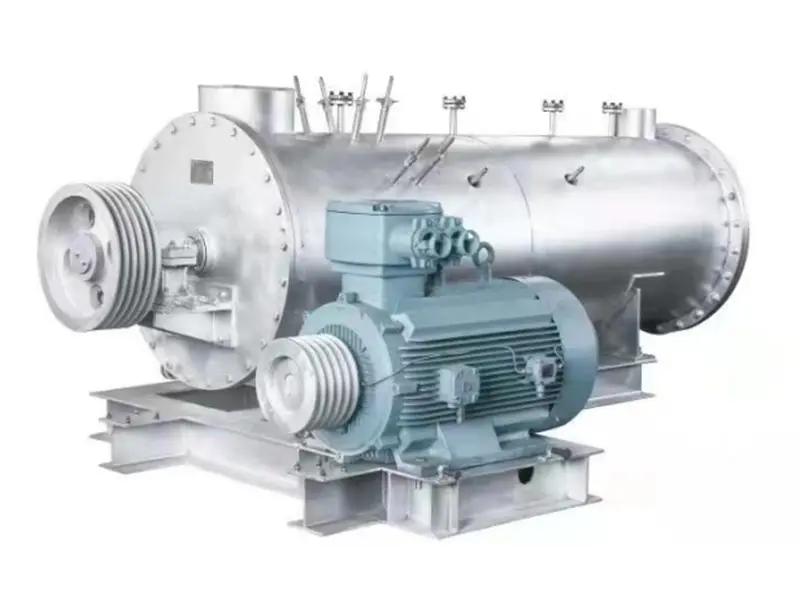
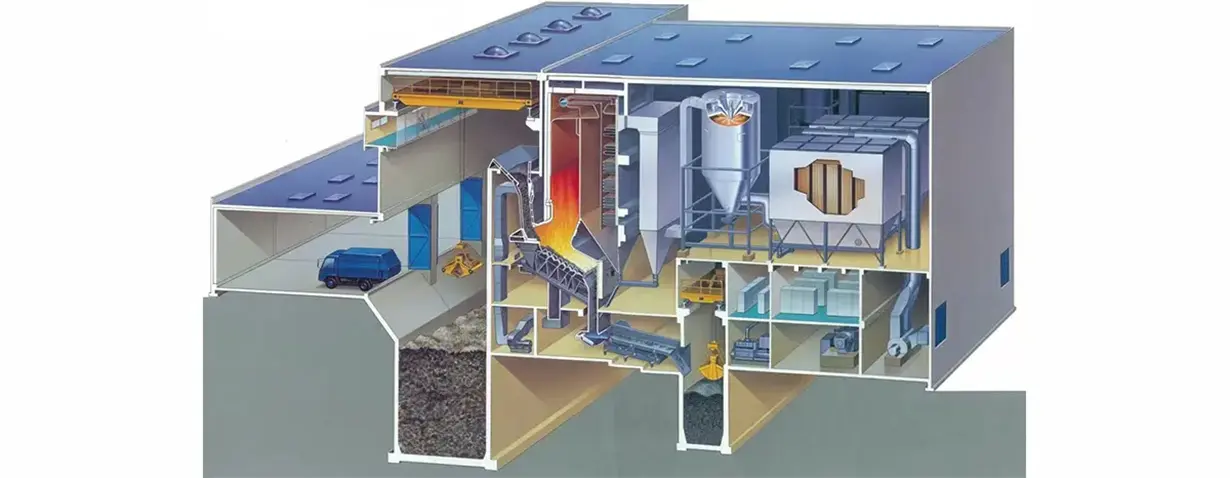
The waste to energy is composed of garbage incinerator, waste heat boiler, flue gas duct, denitrification system, deacidification tower system, dust collector system, boiler auxiliary machine, etc. The garbage is fed into the garbage feeding hopper by the grab, and is pushed into the incinerator by the pusher after passing through the bypass cracking device and the chute.The incinerator grate consists of three parts: the drying section, the burning section and the burning section,the burnt waste ash and dregs are discharged through a slag discharging machine. The high temperature flue gas produced by combustion is discharged from the chimney after it reaches the discharge standard through the waste heat boiler and the flue gas treatment system.